Not every trader thinks about the implementation of recommendations when trading. Many people pay more attention to such important things as:
- Trading strategy;
- Leverage and other conditions.
Once the trade is completed, the trader will only be interested in one thing – whether the trade was profitable. A book and B book is specific terminology that will have to be dealt with in more detail below.

So, it is very important to have an understanding of the difference between the types of forex brokers in order to be successful in forex trading. Many can position themselves as ECN – the A-Book model, but once you see the trading conditions, it will immediately become clear that this technology is out of the question.
There is also a second category of brokers – STP, which in fact turns out to be an ordinary dealing desk, that is, a “kitchen”. However, this scheme also does not always speak of fraud, so do not rush to hang labels.
It is worth understanding in more detail what the A-Book and B-Book order execution models are, what is the difference between them and why the B-Book is not always a bad thing.
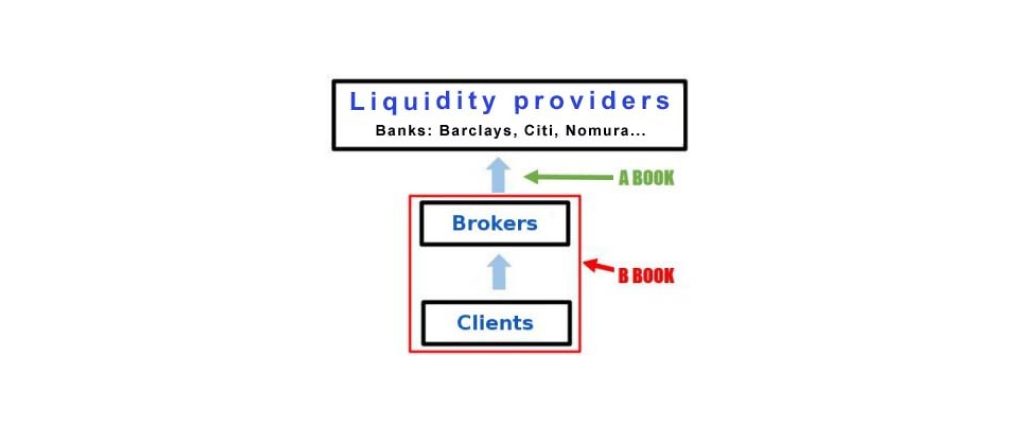
A-Book and B-Book technologies for managing client orders
A prerequisite for a trader’s deal is the presence of a counterparty in the chain of its execution: if someone buys an asset, then there is someone who should sell it. Both models differ in who this counterparty is and where he comes from:
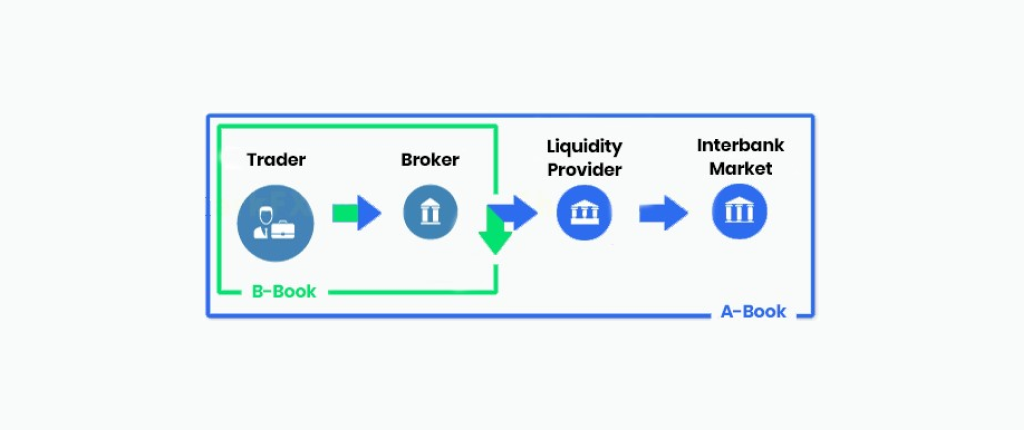
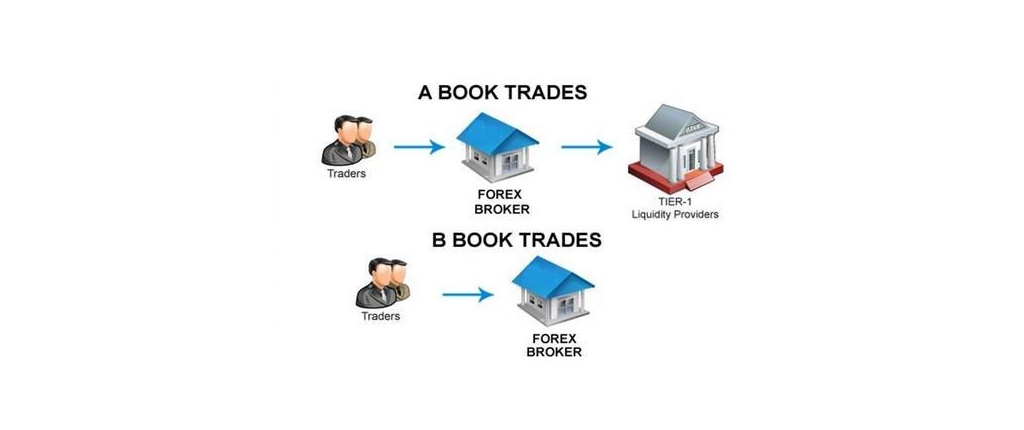
In the A-Book model, as a rule, all of the trader’s orders are forwarded by the trader to the liquidity provider, which then redirects them to the interbank market. The broker’s earnings are formed by a commission for a fixed volume of transactions, as a rule, for 1 lot. It also includes the markup for the spread and the so-called markup.
A trader in this scheme appears only as an intermediary. The ultimate counterparty to the transaction is traders, whose opposite orders are displayed on the interbank market or a liquidity provider.
The “kitchen” is a model in which a trader acts as a counterparty to trades. In other words, traders’ deals are not taken anywhere outside the framework of the broker’s platform. There is also another name for this model – “kitchen”.
There is no conflict of interest in the case of the A-Book. The trader is only an intermediary who provides financial services for his benefit. All in order for the trader to increase the turnover and volumes, bringing the broker even higher commission income.
Many forex brokers often associate the B-Book model with a scam. The thing is that the broker itself acts as a counterparty in it. This causes a conflict of interest since the trader tries on not only the role of an intermediary but also a counterparty. In this scheme, the trader makes money while the trader takes a loss.
It may be interested in displaying non-market quotes in the terminal, peeping through the MT4 add-on behind the set client stops and knocking them down with plugins on the server-side of the platform – to do everything to make the trader lose money.
Despite all of the above, many forex brokers use the B-Book model and are not even silent about it. The fact is that in order to bring client orders to the external market, you need to conclude agreements with a liquidity provider (and, as a rule, more than one), obtain licenses, provide technological support – all these are costs that the A-Book broker is forced to “beat off” at the expense of high markup to the spread.
It physically cannot compete with the B-broker, which does not have all these costs. Traders, in turn, do not really understand all these models, preferring more favorable conditions and thereby, on the contrary, stimulating the emergence of such “kitchens”.
It should be noted that if a forex broker works according to the B-scheme, this does not mean that he is a “kitchen”, but such a possibility exists. Rather, it indicates that the small trades broker is offsetting within their platform, while large trades, singly or in a pool, can be output to the liquidity provider and then to the interbank Forex.
This is called the combined or hybrid A-Book and B-Book model. An example of such a model is a combination of a cent (B-Book) and ECN (A-Book) accounts. There is no conflict of interest in this model since the book broker does not act as a counterparty to transactions.
Should you avoid B-brokers? The question is ambiguous, and here logic comes in. It is quite logical that transactions with a volume of 0.01 lots will not be withdrawn from the internal brokerage system. It is much easier to overlap such transactions internally, or then the broker will withdraw it at a loss.
Although the forex brokers with the A-Book model are just more interested in maintaining its reputation, for this reason, it is more likely to operate in a hybrid scheme. And this will avoid its participation in the chain in the role of a counterparty.
On the other side, B-Books are much more dangerous, unlike A-Book. If we compare with the volumes of interbank transactions, then the internal volumes on the broker’s platform are a mere trifle. And if a large client places a large order within the system, the forex broker will have to act as a counterparty. Or allow slippage.
Both options are signs of a “kitchen” that do not bring anything good to traders. Therefore, it is best to avoid pure B-Book brokers.
Hybrid model
Many companies are resorting to a hybrid model book store, using both A-Booking and B-Booking at the same time.
Thus, they further increase their profitability.
This is done simply: 10% of profitable traders are brought to the real market, and 90% of unprofitable traders remain to trade within the broker.
Here are some criteria for losing traders:
- Choosing the maximum leverage.
- The risk is more than 10% of the deposit in one transaction.
- No stop losses.
- Small deposit.
Considering the above, I think it is not difficult to create some kind of algorithm that determines potentially profitable traders.
And everything would be fine if not for one problem.
Profitable traders are still someone’s loss.
And hybrid book brokers send extremely profitable traders to liquidity providers, creating a so-called “toxic stream”.
When a liquidity provider receives such a toxic flood, it degrades the execution quality for that broker. Forex brokers, in turn, will feel this in the form of frequent slippage.
What is better?
Many traders are learning towards the B book broker model because it’s less risky for them. It’s okay if you are trading with a B book broker. This doesn’t affect trading and allows you to withdraw profits, great prices, etc. Interest in this model is caused for a reason.
This system used by Market Maker “Dealing Desk” brokers is known as “B booking”. ECN / STP brokers without a dealing desk send all their clients’ trades to the live market or to liquidity providers.
In addition, there is a lot of competition among forex brokers, and many B-brokers have started to allow traders to participate in tournaments and trade normally. Each book broker can easily make money using this model without risk by increasing the spread or charging a commission on the volume of orders.










